Air Classifier
The realization of powdered material functionality often requires the particle size to meet certain conditions. For example, Zirconia powder for ceramic glaze requires an average particle diameter of 1-2 microns. Metal powder for 3d printing requires good sphericity, fine particle size and narrow particle size distribution. It is necessary to classify the powder particles to meet for specific applications.
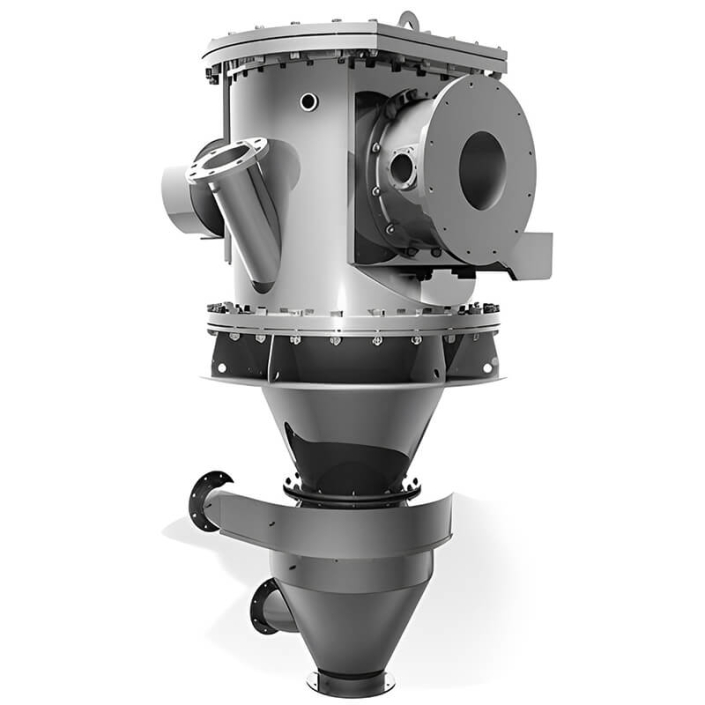
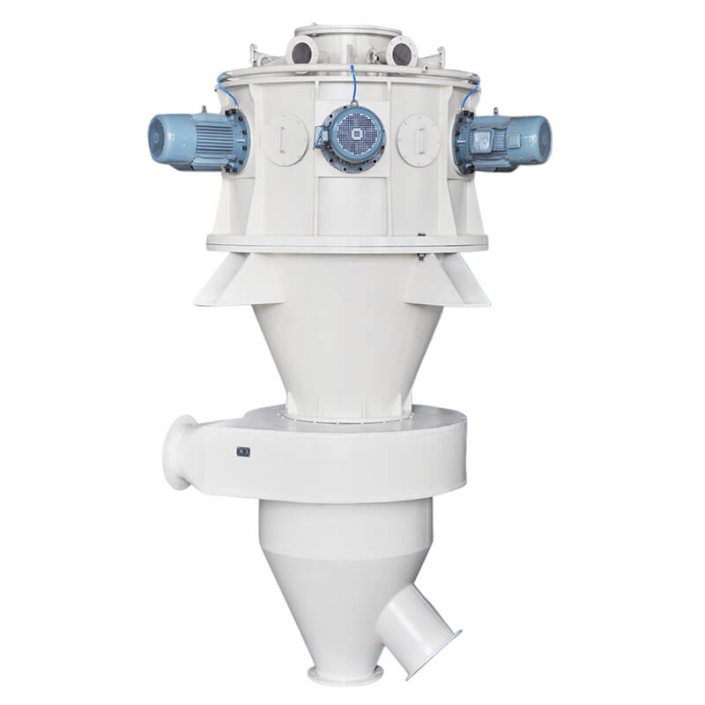
Classification is the operation of separating the powder into two groups of large and small particles. In an air classifier, the powder is subjected to air resistance and centrifugal force, thus accomplishing the operation of classifying ultra-fine powders.
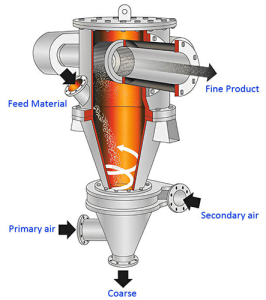
Air Classifier Working Principle
- The materials enter the classification area with the rising airflow.
- Under the strong centrifugal force generated by the classifying wheel, the coarse and fine particles are separated.
- Fine particles enter the cyclone separator through the classification wheel.
- The other particles drop to the secondary air inlet.
- Coarse and fine particles are separated again through the secondary air.
- Rejected material is discharged at the bottom of the classifier.
Features
- Super fine classification at micron-level, suitable for spherical, flake, and needle-like particles
- Particle size cut-point in the range 1 to 100 microns
- Precise on-stream control of cut-point by variation of rotor speed and airflow
- High classification efficiency up to 90%
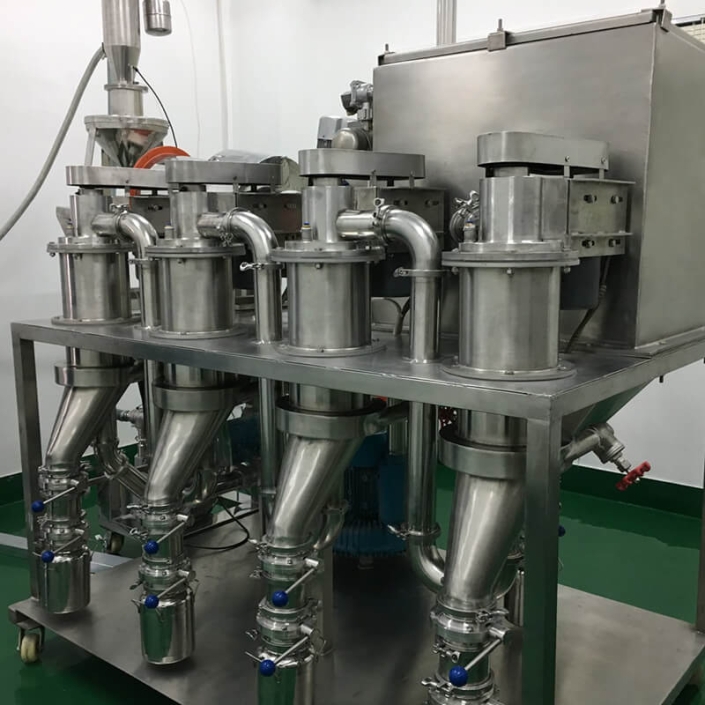
- Multiple classifiers can be used in series for multiple particle size ranges at the same time.
- PLC control, real-time monitoring of the running
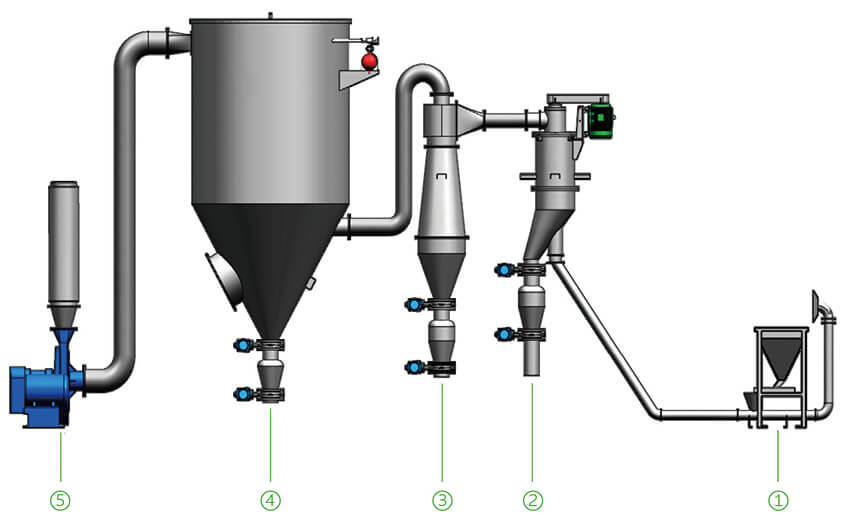
Air Classifier diagram
| 1. Feed Hopper | 4. Filter Collector |
| 2. Air Classifier | 5. Extractor Fan |
| 3. Cyclone Separator |